Lactose Intolerance
WHAT IS LACTOSE?
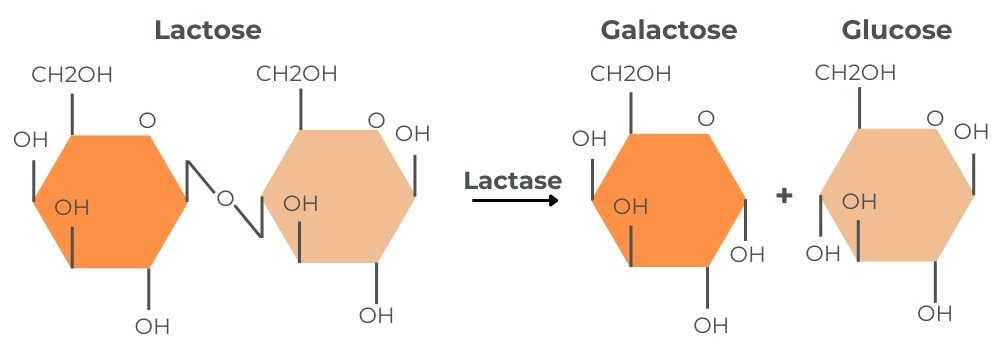
Lactose is a sugar (carbohydrate) found exclusively in mammalian milk. It is a disaccharide (two sugar molecules) composed of one glucose molecule and one galactose molecule linked by a β-1,4-glycosidic bond.
Carbohydrates can only be absorbed as monosaccharides (single sugar molecules) in the small intestine. The enzyme lactase first breaks down lactose into glucose and galactose for absorption.
WHAT IS LACTASE?
Lactase, also known as lactase-phlorizin hydrolase (LPH), is an enzyme located in the brush border of the small intestine. It facilitates the breakdown of lactose into glucose and galactose.
Lactose broken down by lactase into galactose and glucose.
WHAT IS LACTOSE INTOLERANCE?
Lactose intolerance refers to the symptoms that occur when the body cannot digest lactose properly due to insufficient lactase activity in the small intestine.
Mechanisms Behind Symptoms:
1. Osmotic Effect: Unabsorbed lactose draws water into the intestine, increasing intestinal contents and speeding up gut movement (peristalsis).
2. Colonic Fermentation: Gut bacteria ferment unabsorbed lactose, producing short-chain fatty acids and gas, which can cause bloating and distension.
SYMPTOMS OF LACTOSE INTOLERANCE
Symptoms vary based on the amount of lactose consumed and the extent of lactase deficiency. Symptoms typically appear when lactase activity drops below 50%. However, many individuals can tolerate up to 12 grams of lactose, roughly equivalent to one glass of milk.
Common Symptoms:
Abdominal cramping and pain
Bloating and distention
Increased flatulence
Stomach gurgling
Loose stool
Diarrhoea
Nausea (less common)
Constipation (less common)
WHAT CAUSES LACTOSE INTOLERANCE?
1. Primary Lactase Deficiency
A gradual decline in lactase activity starts once breastfeeding ends.
Prevalence varies significantly by ethnicity due to evolutionary adaptations.
Prevalence by Ethnicity:
Asian populations: 95-100%
Native Americans: 80-100%
African Americans: 50-80%
Hispanic populations: 50-80%
Southern Indian subcontinent: 60-70%
Northern European (e.g., Scandinavia, Netherlands): 15%
2. Secondary (Temporary) Lactase Deficiency
Caused by gastrointestinal illnesses or conditions that cause significant damage to the brush border of the small intestine or significantly increase bowel transit time.
Common Causes:
Infections and Parasites: Rotavirus, Giardia lamblia, Cryptosporidium parvum and Entamoeba histolytica.
Organic Diseases: Coeliac disease, Crohn's Disease
Surgical Procedures: Gastric bypass surgery, Nissen fundoplication (reflux surgery), Small bowel resection
Other: Radiation therapy, cystic fibrosis
3. Congenital Lactase Deficiency
It is a severe and rare genetic disorder where babies are born without the ability to produce lactase. Symptoms appear shortly after birth once breastfeeding has commenced.
4. Developmental (Neonatal) Lactase Deficiency
Lactase production begins around 34 weeks of gestation. Due to underdeveloped intestines, premature infants may have temporary lactase deficiency.
DIAGNOSIS OF LACTOSE INTOLERANCE
Lactose Challenge:
The easiest way to diagnose lactose intolerance is to consume a large amount of lactose (e.g., a milkshake) and observe symptoms. Temporary elimination and reintroduction can help to assess tolerance.
Hydrogen Breath Testing:
Ingest a dose of lactose, usually 20-50g (the equivalent of 400mL - 1000mL cow's milk), and measure hydrogen breath levels at 30-minute intervals. Increased hydrogen levels indicate poor lactose digestion.
Hydrogen breath testing does not exclude secondary causes of lactase deficiency, such as Coeliac Disease or Crohn's Disease.
Jejunum Biopsy:
The gold standard for determining lactase activity is a biopsy of the jejunum (the middle part of the small intestine). This highly invasive procedure is rarely performed.
Genetic Testing:
Identifies four genetic variations that regulate lactase production. It helps distinguish between primary and secondary lactase deficiency but does not measure the level of lactose tolerance.
DAIRY & BONE HEALTH
Importance of Dairy in the Diet
Cow's milk and its dairy products are unique in that they are the primary sources of calcium in the diet. Dairy products include other essential nutrients:
Macronutrients: Protein, carbohydrates, fat
Vitamins: A, B12, riboflavin
Minerals: Calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, potassium, zinc.
Excluding dairy makes meeting calcium requirements challenging, increasing the risk of deficiency.
Calcium's Role in the Body
Functions: Calcium is essential for building and maintaining bone strength and structure. It also plays a vital role in heart and nervous system function, muscle contraction, and blood clotting.
Storage:
99% in bones and teeth
<1% in blood (tightly regulated)
The body carefully regulates blood calcium levels to keep them stable. When dietary calcium is insufficient, the body pulls calcium from the bones. Over time, this can lead to brittle bones and a higher risk of developing osteoporosis (porous bones). During childhood and adolescence, calcium is deposited into the bones, with peak bone density reached by the early twenties. After that, calcium is gradually lost from the bones, especially women after menopause. Getting enough calcium through your diet is essential for maintaining bone health at all stages of life.
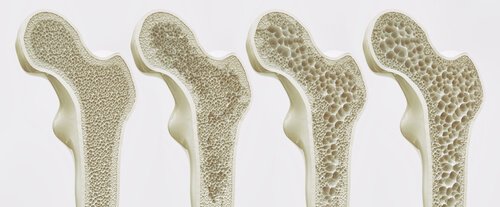
Stages of Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis and Bone Health
Osteoporosis is a condition in which bone structure is compromised, bones become weak, less dense, and prone to fractures. It is common in Australia, affecting an estimated 1.2 million people, with a further 6.3 million people experiencing low bone density. Poor bone health contributes to 183,000 broken bones each year.
Challenges in Diagnosing Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is often referred to as a "silent disease" because it usually progresses without noticeable symptoms in its early stages. In many cases, the first indication is a bone fracture.
Osteoporosis is diagnosed with a bone density scan, also called a DEXA scan. This simple test measures bone density using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry.
MANAGEMENT OF LACTOSE INTOLERANCE
Managing lactose intolerance does not require eliminating all milk and dairy products. Options include:
Lactose-free milk and yoghurt
Hard cheeses, which naturally contain low levels of lactose
Lactase enzyme drops to create your lactose-free products at home
Probiotic supplementation
WHAT TO DO IF DAIRY IS TROUBLING YOU
1. Consult your GP for evaluation and assessment to rule out secondary causes of lactase deficiency, such as underlying medical conditions.
2. Work with a Gut Health Dietitian to determine if symptoms are caused by lactose, another component in milk, or other dietary factors.
The severity of symptoms of lactose intolerance depends on several factors, including:
The amount of lactase produced by the intestines
The quantity of lactose consumed
Foods eaten alongside lactose-containing foods
The composition of the gut microbiota
Gastrointestinal motility
Intestinal hypersensitivity
KEY POINTS
Lactose intolerance does not require complete lactose or dairy elimination.
Lactose does not cause damage to the body, unlike conditions such as undiagnosed Coeliac Disease and Crohn's Disease
Inadequate calcium intake increases the risk of low bone mineral density, osteoporosis, and fractures.
REFERENCES
Healthy Bones Australia. (n.d.). Retrieved December 2, 2024, from Osteoporosis Prevention - Healthy Bones for Life without Fracture
Heyman, M. B., & Committee on Nutrition. (2006). Lactose intolerance in infants, children, and adolescents. Pediatrics, 118(3), 1279–1286. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2006-1721
Leis, R., de Castro, M. -J., de Lamas, C., Picáns, R., & Couce, M. L. (2020). Effects of Prebiotic and Probiotic Supplementation on Lactase Deficiency and Lactose Intolerance: A Systematic Review of Controlled Trials. Nutrients, 12(5), 1487. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051487
Rachwał, K., Wielgus, K., Bator, P., Razik, W., Łyko, G., Antos, M., Furgalska, J., Pawłowska, M., & Wawryszuk, A. (2024). Lactase Deficiency and Lactose Intolerance: Current Understanding and Future Directions. Journal of Education, Health and Sport, 69, 49393. https://doi.org/10.12775/JEHS.2024.69.49393
Wanes, D., Husein, D. M., & Naim, H. Y. (2019). Congenital Lactase Deficiency: Mutations, Functional and Biochemical Implications, and Future Perspectives. Nutrients, 11(2), 461. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11020461